Collection Framework
首先根据图片感受一下整个collection的架构.
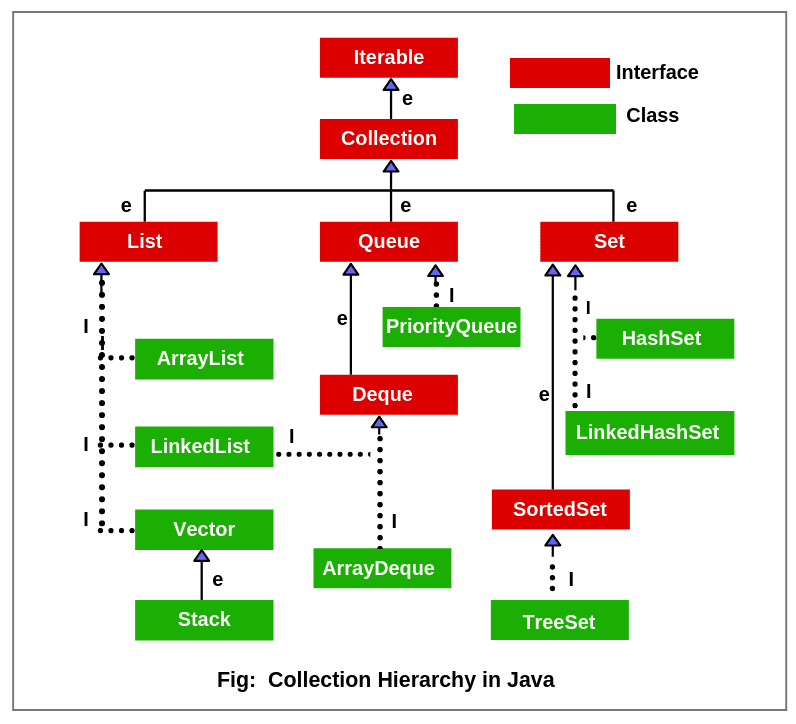
Iterator Interface
Collection接口扩展了Iterable接口, 目的还是为了操作其中的Iterator<T> iterator();这里主要关注Iterator而不是Iterable. 主要的抽象方法就是前两个, 如果c是某个对象, 用的时候一般直接写Iterator<String> iter = c.iterator();, 再通过这两个方法遍历.
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
default void remove() { //删除上一个next返回的元素
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
}
Collection Interface
Collection接口最主要就是定义了增删的功能, 也可以判断元素是否存在等. AbstractCollection类去实现了Collection接口的一些通用的方法, 保留size和Iterator为抽象方法.
List Interface
List接口继承了Collection接口, 并且定义了一些随机访问的方法, 比如增删改查: void add(int index, E element);, E remove(int index);, E set(int index, E element);, E get(int index);.
而AbstractList类去继承了了AbstractColle 1ction类, 并且实现了List接口. 后面的ArrayList则继承了这个AbstractList, 而LinkedList通过继承AbstractSequentialList, 再继承AbstractList.
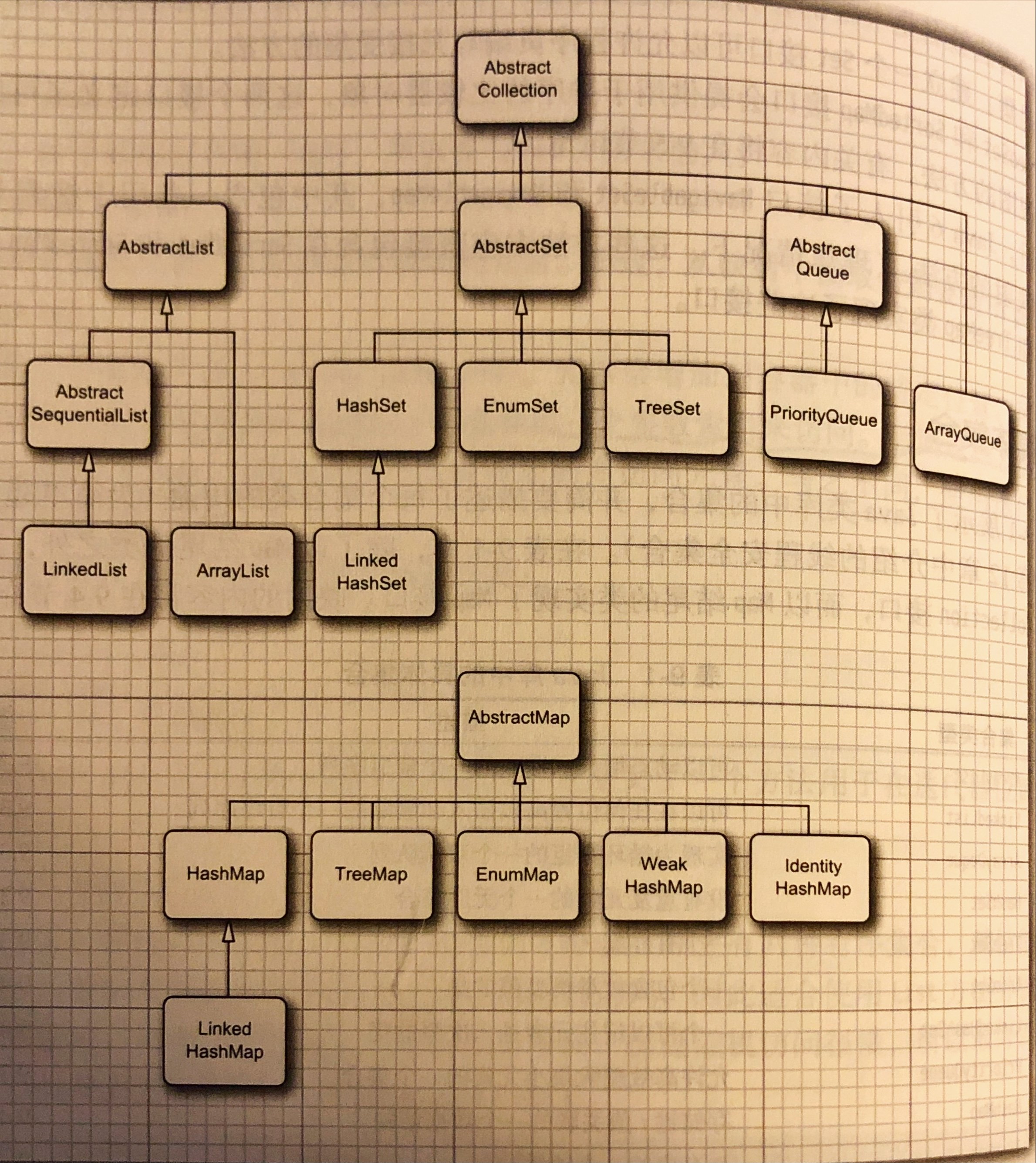
这两个List都声明了public ListIterator<E> listIterator(), 可以用来反向遍历.
ArrayList
值得注意的一点是, ArrayList继承了RandomAccess, 说明它是支持随机访问的. 判断的时候就可以用if (list instanceof RandomAccess)来知道其是否是RandomAccess的实例, 从而判断是否可以用Collections.indexedBinarySearch(list, key), 否则就只能用Collections.iteratorBinarySearch(list, key).
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
//初始容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//空实例数组
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//对应默认无参构造器, 和大小为0的ArrayList区分
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//存储数据的地方
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
//ArrayList大小
private int size;
//构造器
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);
}
}
//无参构造器
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
// 指定的集合作为参数的构造器
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray(); //转换为数组
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[]. Object[]数组默认为null
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// 不是Object就替换成空数组.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
//将ArrayList容量减小到实际包含数据大小
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
//扩容, 可以用来提前声明好所需空间, 避免重复扩容(内部没有用过, 是给用户用的)
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
//所需的最小容量大于已申请的最大容量(10)
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
//求最小扩容的容量大小
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);//选择默认初始容量和现在需要容量的大者
}
return minCapacity;
}
//求最小扩容的容量大小
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++; //迭代器遍历的时候, 会检查这个值, 防止其他线程对这个ArrayList有了修改, 重复度
//overflow-conscious code -> 意思就是说忽略溢出, 如果minCapacity - elementData.length
//溢出int范围, 那么执行不了
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity); //扩容算法
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//真正的扩容算法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //新容量是旧容量的1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) //依然小于所需容量, 直接让新容量等于所需容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) //是否超出定义的MAX_ARRAY_SIZE最大容量, 若超过, 通过minCapacity用hugeCapacity去判断返回Integer.MAX_VALUE还是MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//这里看到ArrayList添加元素的实质就相当于为数组赋值
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//从index开始之后的所有成员后移一个位置, 将element插入index位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index); //源数组, 起始位置, 目标数组, 目标数组中的起始位置, 长度
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
}
copyOf是浅拷贝, 用int这种基本类型没法测试. 但是数组如果存的是对象, 那么实际上复制的是指向对象的引用(对象的地址). 但是修改复制后数组, 把引用换成了新的, 并不会对对象内部进行修改.
LinkedList
本质是双向链表. 实现了List和Deque, 所以可以当成栈和队列的实现基础.
Deque接口继承了Queue接口, queue接口实际上就是包含了增删改查, 而Deque将其扩展成了针对头尾的增删改查.
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
//头尾指针
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
public LinkedList() {
}
//将集合中的元素添加进LinkedList
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
//连接e到链表的头
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); //前面连null, 后面连f
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//连接e到链表的尾
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//连接e到某个结点的前面
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//删掉头结点并返回头中实际的item
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删掉尾结点并返回尾中实际的item
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删掉某个结点
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//返回头结点的item
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
//add带返回值
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//删掉某个结点, 有相等的就删除第一个
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//将集合插到链表的尾部
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
//将集合插到指定位置
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) { //插入的位置其实是尾部
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);//插入位置的前后结点
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
//链表的结点
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
最后总结一下方法. 增:
add()就好, 成功会返回true.offer()与add等价.push()与addFirst()等价; 删:remove()若为空会报NoSuchElementException, 而poll会返回null.pop()与removeFirst()等价; 改:set()会先检查index, 如果合法就可以添加. 并返回老的item值; 查:getFirst()和element()等价, 如果链表为空会报NoSuchElementException, 而peek()会返回null;
Set Interface
主要有三种实现类HashSet, LinkedHashSet(HashSet的子类, 可以按照添加顺序遍历元素), TreeSet(可以对元素进行排序). Set本身如下.
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> {
// Query Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Operations
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
// Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
}
HashSet
本质上还是利用了HashMap. 添加元素的时候, 会用该元素的hashCode()计算哈希值, 如果该哈希值没有其他元素, 就可以成功添加. 如果有元素, 就用equals()比较.
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; //value用Object替代
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
/**
* HashSet的本质还是HashMap
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
//用初始集合构造HashSet
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* the specified initial capacity and default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
}
LinkedHashSet存放依然是无序的, 但是在添加元素的时候用了双向链表来链接不同元素. TreeSet底层是红黑树, 自然排序就要去实现Comparable接口, 自定义排序就要实现Comparator接口, 直接把Comparator的实现对象当做构造器的参数.
Map Interface
主要被HashMap(和子类LinkedHashMap), TreeMap(用key排序), Hashtable实现. Map的一对key-value共同构成了一个Entry对象.
public interface Map<K,V> {
// Query Operations
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
// Modification Operations
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Object key);
// Bulk Operations
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void clear();
// Views
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
interface Entry<K,V> {
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
}
public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());
}
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());
}
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());
}
}
// Comparison and hashing
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
// Defaultable methods
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
}
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
}
default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Objects.requireNonNull(function);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
// ise thrown from function is not a cme.
v = function.apply(k, v);
try {
entry.setValue(v);
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
}
}
default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
V v = get(key);
if (v == null) {
v = put(key, value);
}
return v;
}
default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
remove(key);
return true;
}
default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
put(key, newValue);
return true;
}
default V replace(K key, V value) {
V curValue;
if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) {
curValue = put(key, value);
}
return curValue;
}
}
HashMap
jdk7和之前用的是数组和链表实现, jdk8以后是用的数组+链表+红黑树.
对于jdk7之前. 实例化之后, 创建长度是16的数组Entry[] table. 执行map.put(key, value), 通过hashCode()计算key的哈希值. 如果此位置没有元素, 直接放入. 如果为不为空, 则用当前的key去和此位置的链表上的元素进行哈希值比较, 如果都不相同, 则放入; 如果相同再用equals()比较, 返回false就可以插入. 如果返回true就去替换相同key的value. 默认扩容是扩容原容量两倍, 被赋值所有数据到新的数组.
对于jdk8后, 实例化后, 首次调用put()的时候, 才会创建长度为16的数组, 数组是Node[]. 如果当前位置上以链表为形式存在的数据个数大于8并且当前数组长度大于64, 该索引位置上的所有数据就用红黑树存储.
对于hash(), 高低位混合, 我个人觉得是因为做(n - 1) & hash(取余)的时候, 如果n比较小, 那么hash的高位就失去效果了, 所以要异或一下.
长度8才转化红黑树, 源码的解释是树的节点大小通常书链表的爱你干杯, 所以要桶有足够多的节点才转化
JDK1.8后
主要看JDK1.8的源码. 对于hash()来说, 用整个int范围来做是不现实的(空间不允许), 虽然如果哈希映射比较sparse, 遇到碰撞的概率极小, 所以需要取模. 高16位和低16位异或实际上是扰动函数, 使其包含了高位和低位的特征.
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
/* ---------------- Fields -------------- */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
//The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; //默认的初始容量16
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //最大容量
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //填充因子
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; //桶中节点转成红黑树的阈值
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; //桶中节点转成链表的阈值
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; //桶中节点转化为红黑树对应的table的最小大小
transient Node<K,V>[] table; //存数据的数组, 长度必须是power of two
//Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used for keySet() and values()
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
transient int size;
transient int modCount;
int threshold; //The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor). 超过则数组需要扩容
final float loadFactor; //加载因子, 约大则数组存放的数据越密
/**
* Basic hash bin(桶) node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
* 通过entrySet可以得到entry的集合
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; //哈希值
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; //指向下一个节点的指针
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/* ---------------- Static utilities -------------- */
//扰动函数
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); //先赋值, 再异或, 混合哈希值高位和低位
}
//returns a power of two size for the given target capacity. 从高位开始把低位为0的位都变成1, 最后n+1进位, 使大小是2的整数倍
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
/* ---------------- 构造器 -------------- */
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
//Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size(); //m的元素个数
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { //还没有实例化table
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);//超过则需要threshold
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) { //元素放进HashMap中
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 查
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(h ash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
// 增
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
//实际调用只能用public V put
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//table没有初始化或者长度为0就需要扩容
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// n为长度, 根据计算得到i, 也就是应该放入的位置. 与操作其实就是截取了低位(相当于取模), 因为是index, 所以要减1
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // (n - 1) & hash, n是数组长度, -1相当于011111...
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { //桶Node
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//hash相等并且key相等, p其实就是当前桶的第一个值, 觉可以直接插入
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //是红黑树结点
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { //是链表节点
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//超过阈值, 转为红黑树(treeifyBin内部还会判断table长度是否超过64)
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//插入结点的key如果和链表中的某个key相等, 则跳出循环, 否则插入
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) //大小增加后可能会扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); //回调
return null;
}
// These methods are also used when serializing HashSets
final float loadFactor() { return loadFactor; }
final int capacity() {
return (table != null) ? table.length :
(threshold > 0) ? threshold :
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
}
//树节点
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
// Returns root of tree containing this node.
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
}
}
}
红黑树
红黑树不是完美平衡二叉查找树. 维持平衡主要有左旋/右旋/变色的操作. 变色的操作只有在当前节点的父亲是红色, 祖父节点的另一个节点也是红色. 左旋发生在, 当点父节点是红色, 且当前节点是在右子树.
参考
- Javadoc
- collection framework图片
- Java核心技术-卷I
- JavaGuide-Java集合框架常见面试题
- 尚硅谷Java
- JDK源码中HashMap的hash方法原理是什么
- 30张图带你彻底理解红黑树
comments powered by Disqus