工作中遇到了两个坑, 讲述一下心路历程.
toMap
写stream的时候有时会用到toMap来把某个实体的两个字段做一个映射关系. 简单的模拟如下, 没有任何问题.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map =
Stream.of(1, 2, 3).collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(), x -> "value" + x));
System.out.println(map);
}
通常来说, 业务中作为map key的字段是唯一的. 但是因为种种原因, 也会有不唯一的情况, 如下代码. 报错Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key value3.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map =
Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 3).collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(), x -> "value" + x));
System.out.println(map);
}
解决方案是用distinct()抛弃重复的, 或者用3个参数的Collectors.toMap的第三个参数来选取重复key的元素.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map =
Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 3).collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(), x -> "value" + x, (x, y) -> y));
System.out.println(map);
}
也有场景是传入的key确实不是唯一的, key与value是一对多的关系, 那么可以用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map =
Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 3).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity()));
System.out.println(map);
}
Arrays.asList
在写ut的时候中有removeIf这个方法, 按正常业务场景, 传入的值是一个ArrayList, 如下. 没有任何问题, 打印[1, 3].
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.removeIf(x -> x.equals(2));
System.out.println(list);
}
在写ut的时候不想一个一个做add的操作, 于是写了如下代码. 但是却报了Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException的错.
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
list.removeIf(x -> x.equals(2));
System.out.println(list);
}
难道Arrays.asList返回的list不是支持removeIf的list, 于是看底层, 发现返回的就是ArrayList. 百思不得其解, 最后stackoverflow只有发现了坑.
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
再往下挖这个Arrays.asList中的ArrayList, 发现它是Arrays下的一个私有类.
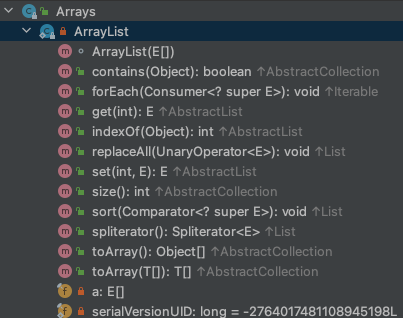
再看Collection接口中的defaultremoveIf方法, 中删除元素的方法底层就是调用了Iterator接口remove.
default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
boolean removed = false;
final Iterator<E> each = iterator();
while (each.hasNext()) {
if (filter.test(each.next())) {
each.remove();
removed = true;
}
}
return removed;
}
而如果不重写remove, 调用时就会抛错.
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
参考
comments powered by Disqus